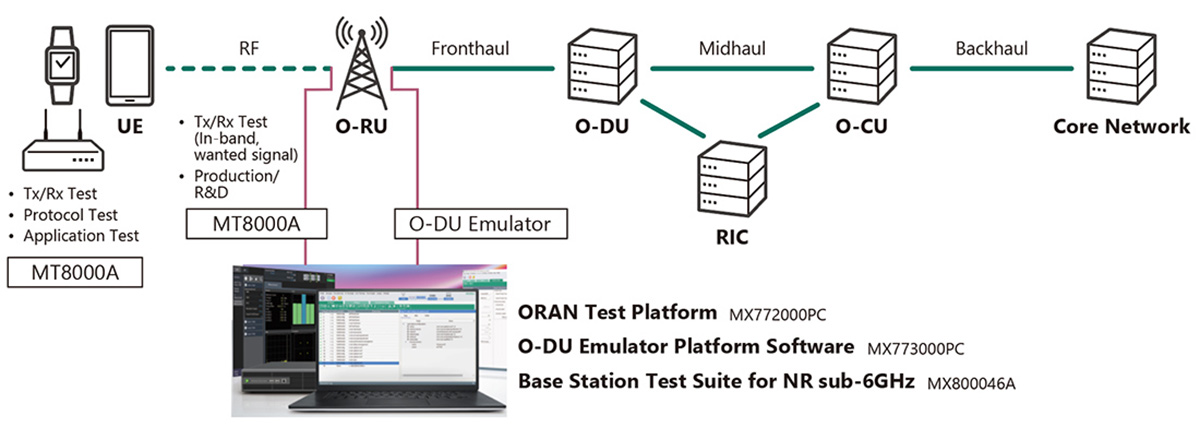
Open RAN telecom networks need testing for each disaggregated component, but that’s not enough. End-to-end testing is also necessary. In How do Open RAN interfaces work?, we covered how Open RAN redefines traditional RAN architecture by disaggregating it into three primary components: the radio unit (RU), distributed unit (DU), and centralized unit (CU). This paradigm…
What is a private 5G network? How does it work?
Private networks have the potential to change many industries and become the primary application for 5G. Processes and protocols make them work.
Ethernet turned 50 in 2023, what’s next?
EE World interviewed John D’Ambrosia, who told a few stories from earlier times and gave a peek at what’s coming next from the IEEE 802.3 set of standards.
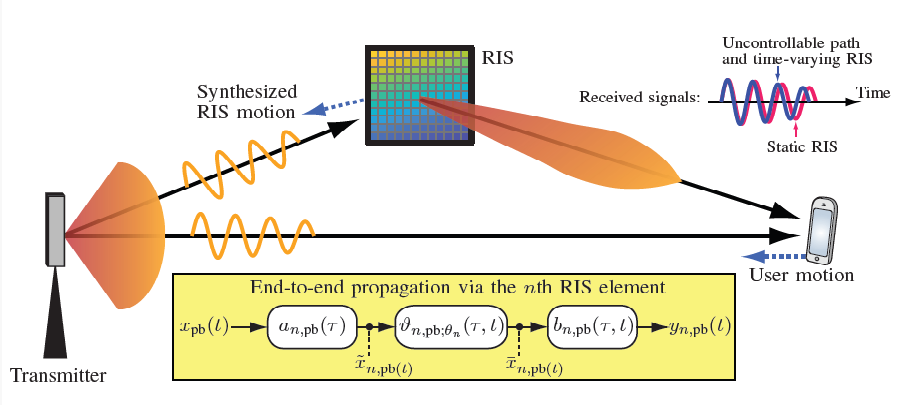
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: what, why, where, and how?
Metamaterial arrays allow the wireless medium and path to be “adjusted” to compensate for its many imperfections and changes.
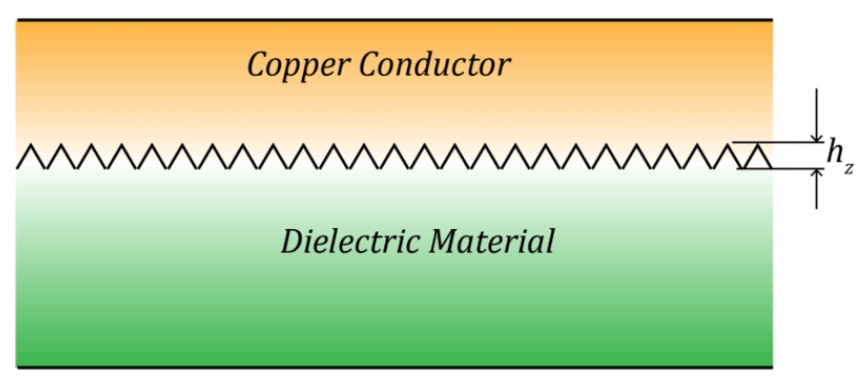
How trace roughness, glass weave, and stackup affect signal integrity
How do circuit board materials and construction affect the integrity of signals that travel across the board?
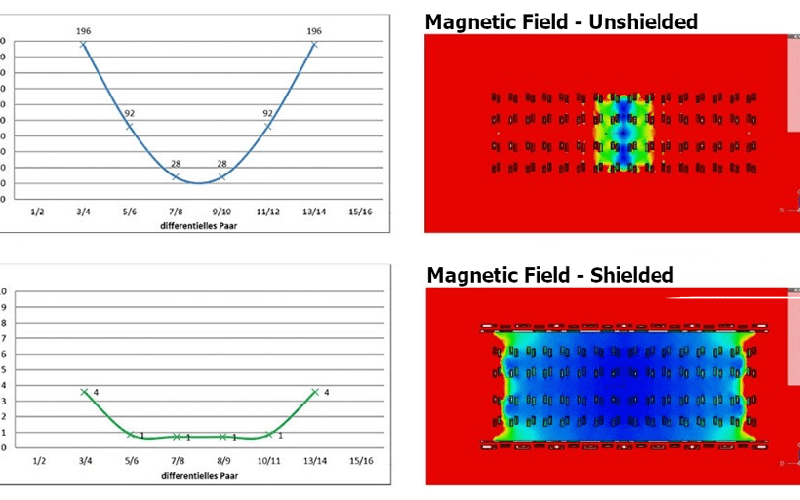
Why is signal integrity crucial for high-speed connector designs?
We discuss the importance of signal integrity, review high-speed deployment challenges, and highlight various connector design strategies to prevent distortion and degradation.
Active baluns bridge the microwave and digital worlds
To achieve the datasheet performance of ultra-high-speed data converters, now clocking to 64 GS/sec, the handoff to and from the microwave domain must be near perfect. To preserve the data converters’ spurious-free dynamic range, a new category of component has been developed that converts between the differential and single-ended signal domains while amplifying and filtering out-of-band signals.
3D printing provides innovative approaches to GHz and THz components
High-precision stereolithography offers an innovative way to create active and passive components for the 100-GHz and even terahertz range.
Video: Research at NYU Wireless and Nokia aims for 6G
Upper mid-band frequencies, above 100 GHz frequencies, and integrated sensing are some of the projects that could find their way into cellular networks. At the 2023 NYU Brooklyn 6G Summit, EE world met with Prof. Sundeep Rangan, associate director of NYU Wireless and Peter Vetter, president of core research at Nokia Bell Labs to discuss…
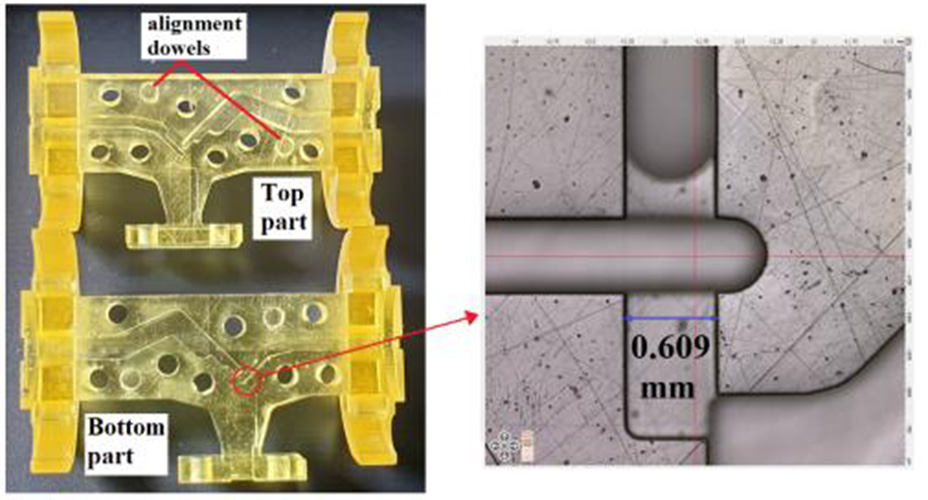
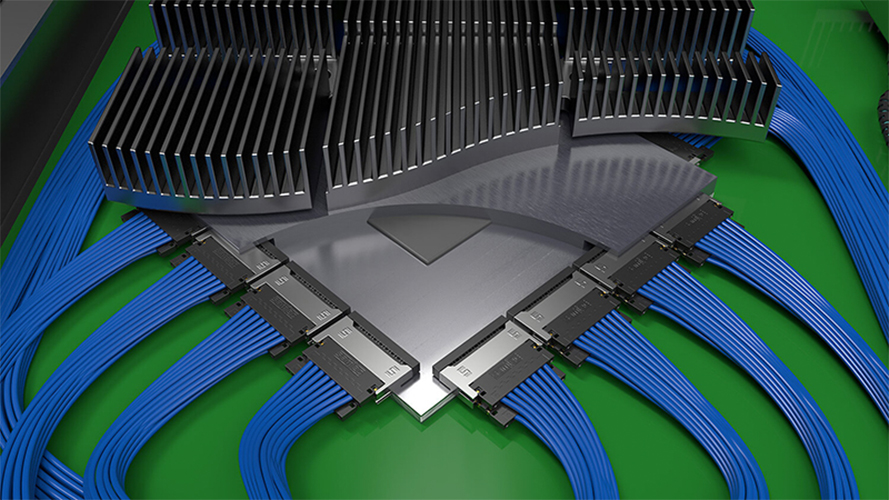
How does a 224 Gbps-PAM4 connector work?
Designing 224 Gigabits per second four-level pulse amplitude modulation (224 Gbps-PAM4) interconnects is challenging. But it’s required to support the demands of generative artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), 1.6 Terabits per second (Tbps) networking, and other high-speed applications in advanced data centers, as well as 5G and 6G communications infrastructure. At these elevated data…