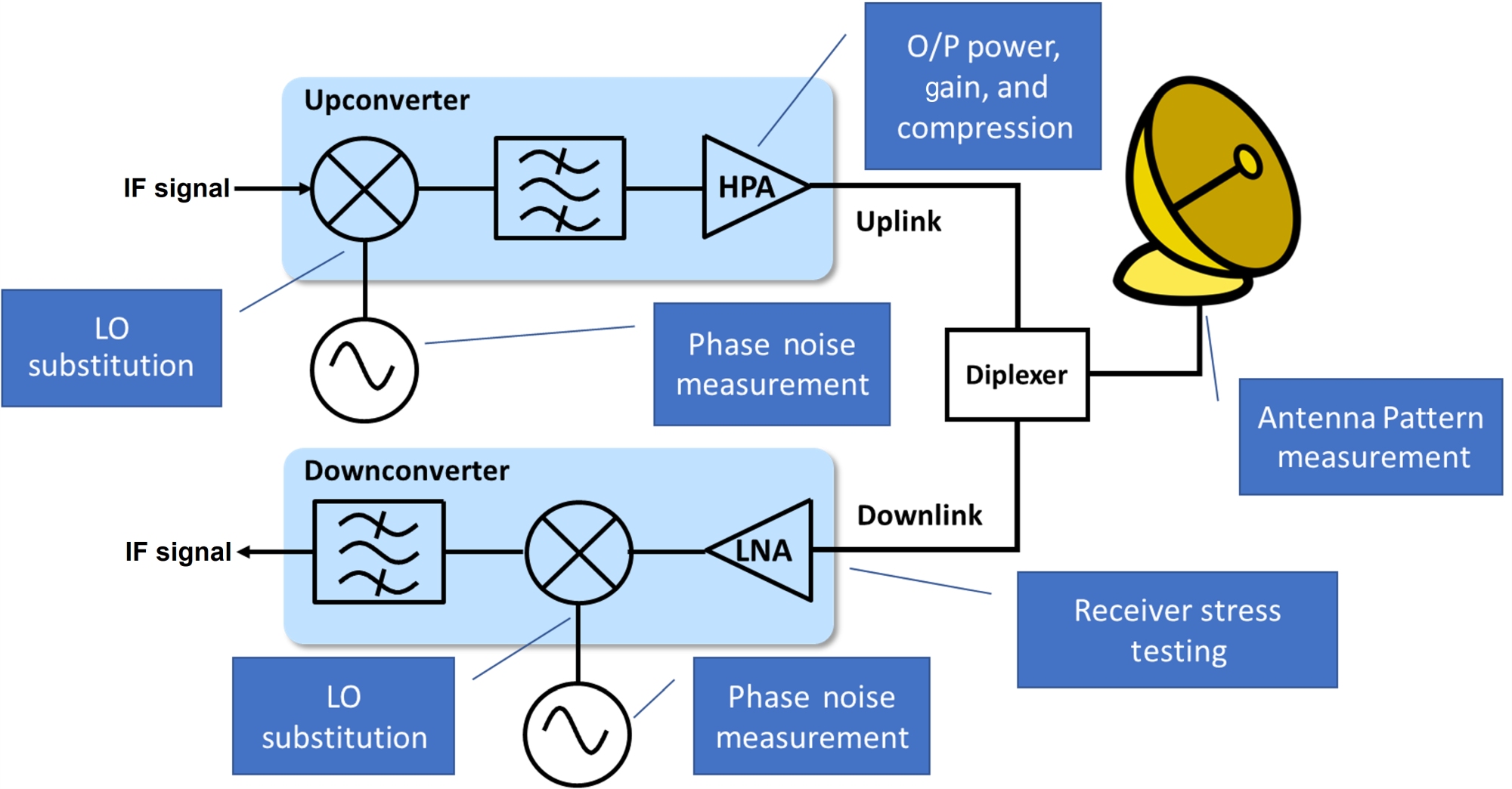
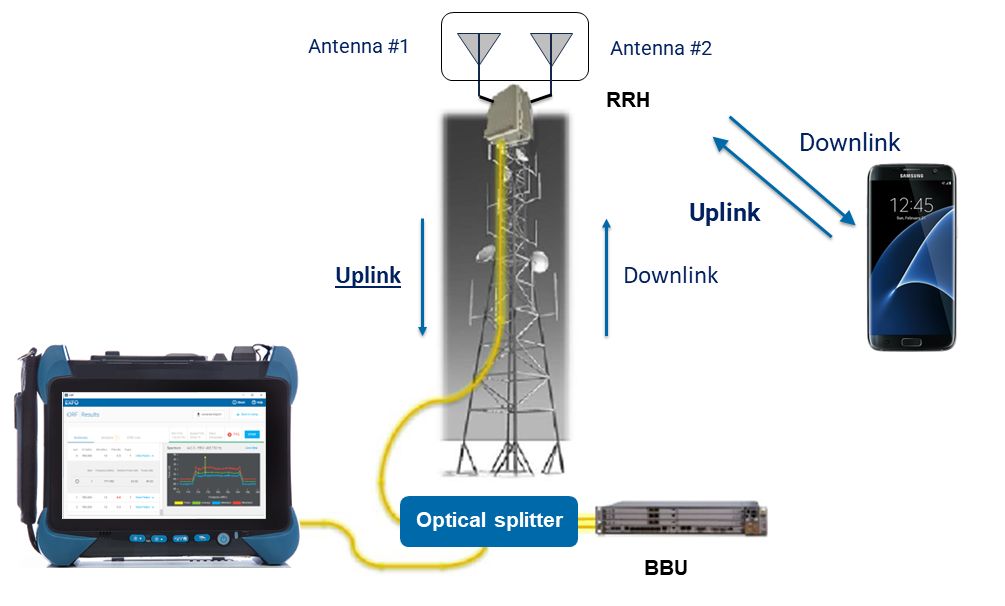
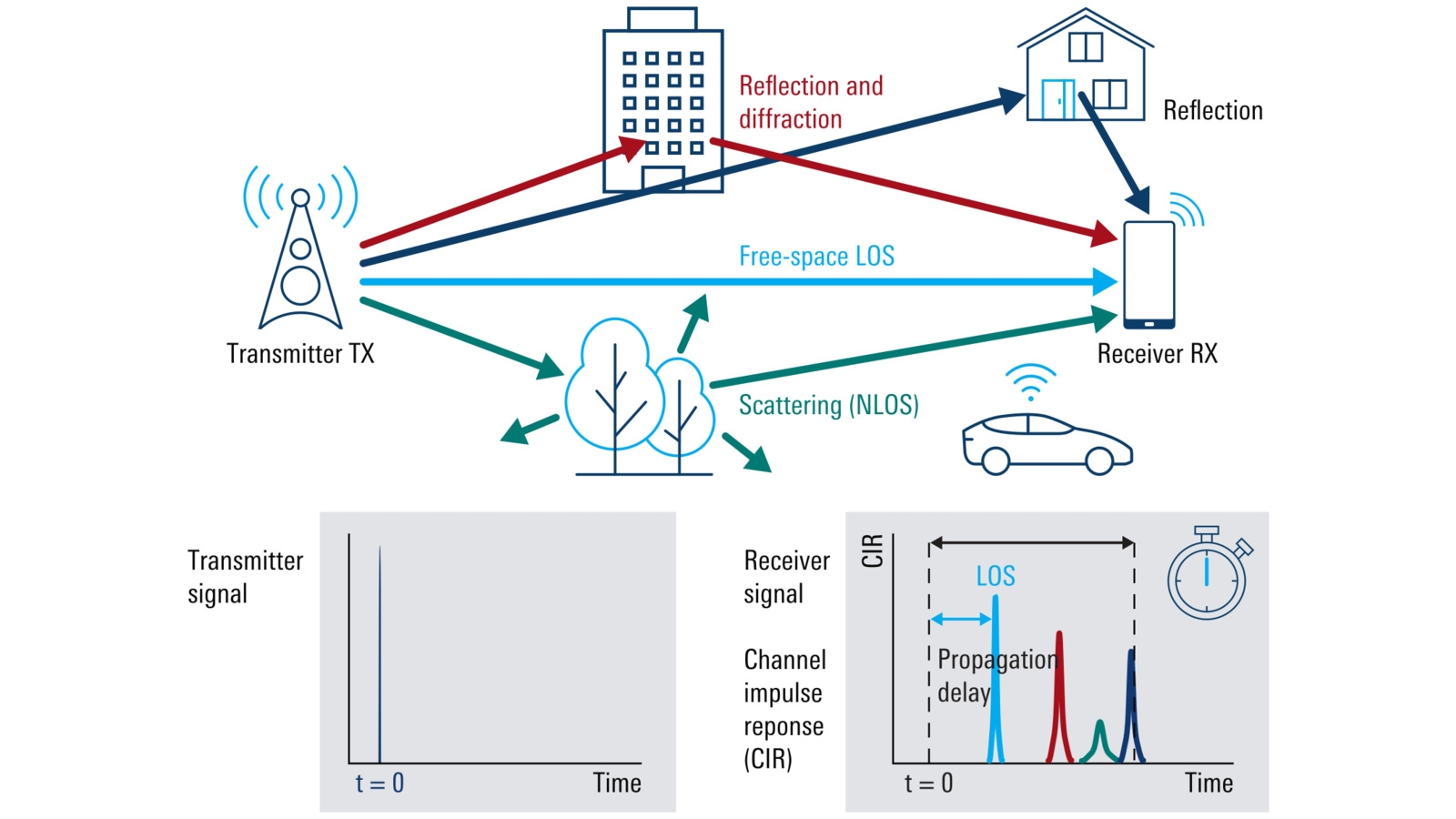
Noise measurement, LO substitution, receiver stress testing, power measurement, CCDF and PAPR characterization, and antenna-pattern measurement play critical roles in link budget, bit-error rate, and SNR requirements. Low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems are being deployed for mission-critical use cases at an accelerating rate. This brings associated critical test requirements that, if not performed accurately, could…
5G mmWave test builds on RF best practices
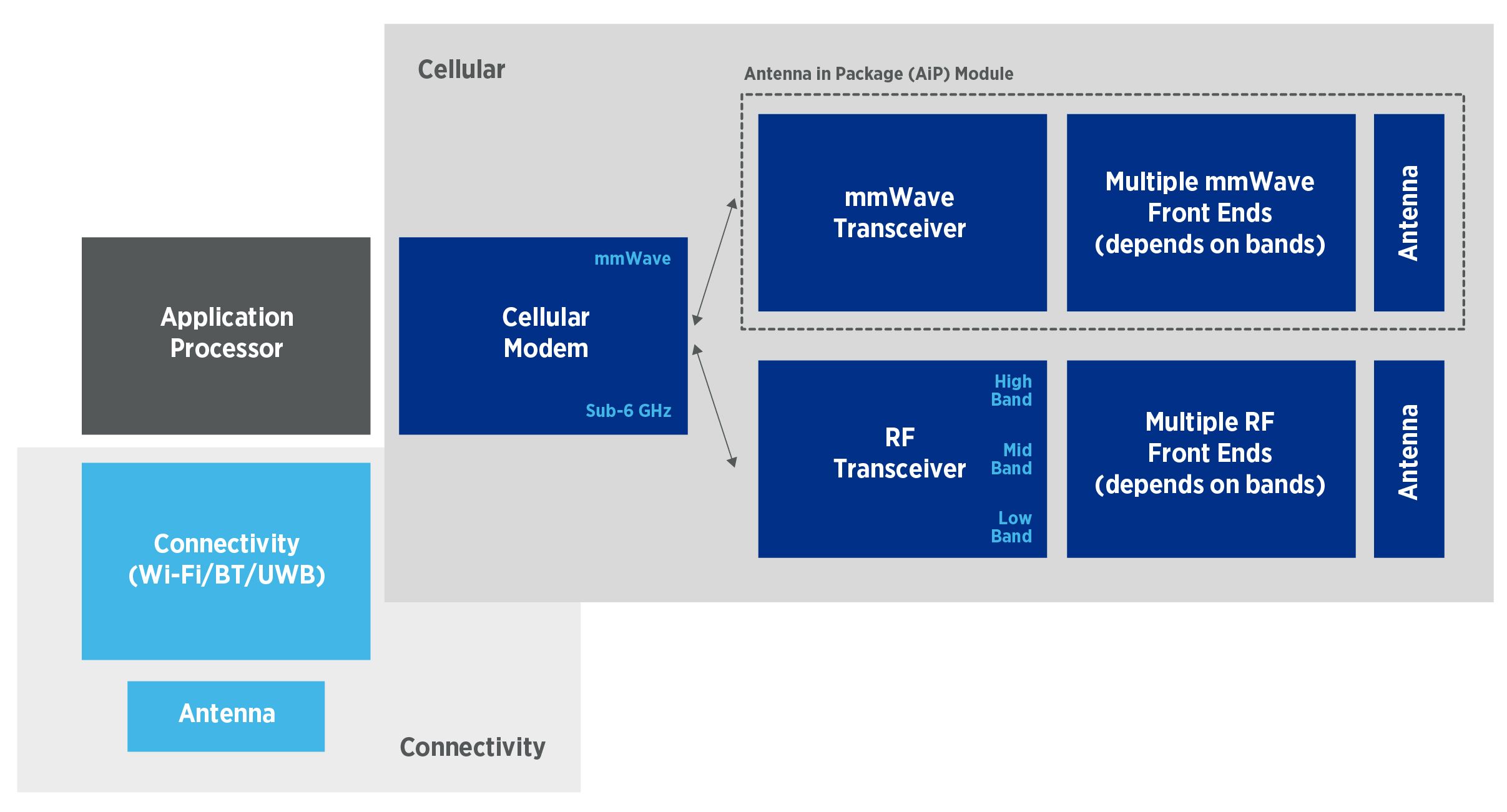
The high level of integration in today’s mmWave phone means traditional test methods no longer apply.
Identify, troubleshoot, and resolve PIM issues in wireless networks
5G brought passive intermodulation problems into the spotlight. Now it’s up to engineers and technicians to identify and mitigate signal degradation to minimize dropped calls and other issues. A loose connection; a metal roof; power lines. Even a rusty bolt. It’s estimated that mobile operators will spend $1.1 trillion on capital expenditure between 2020 and…
How does PAPR reduction improve power amplifier efficiency?
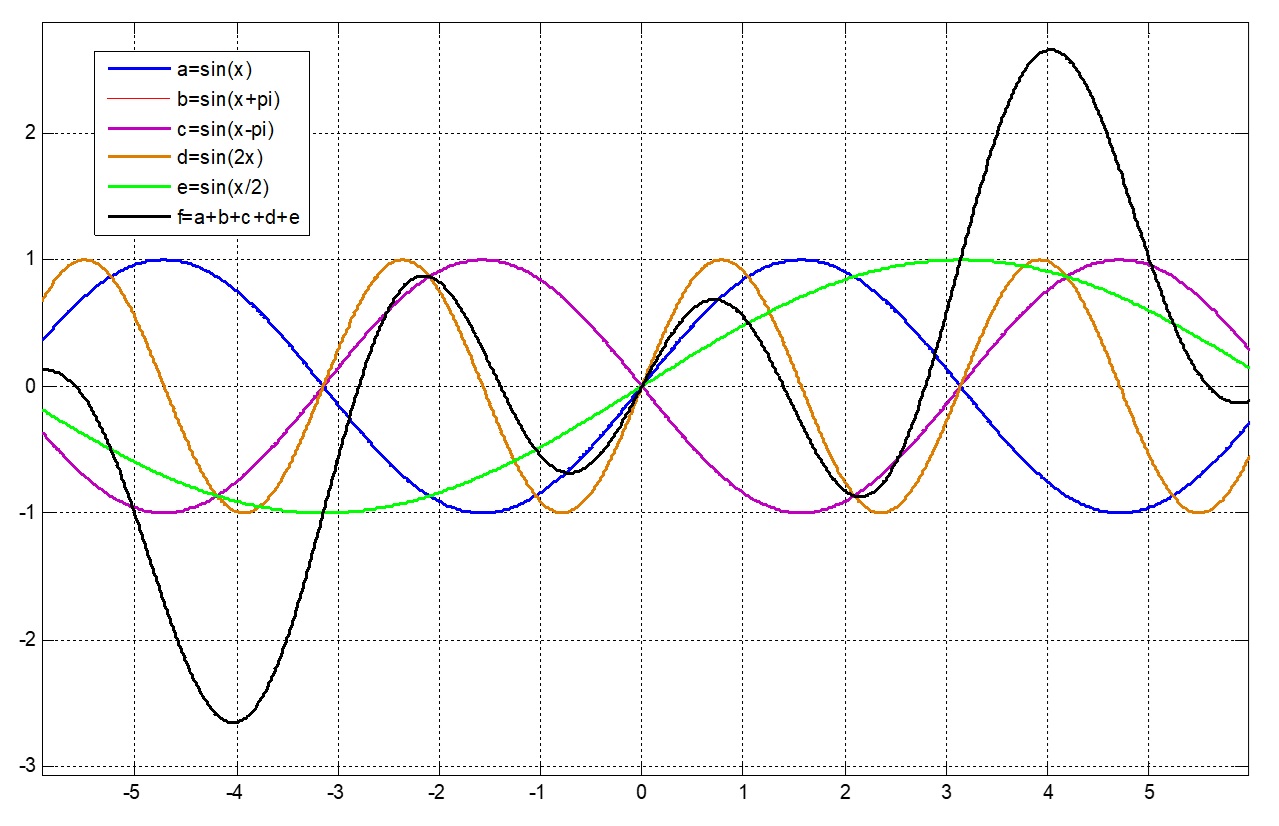
5G’s Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) brings with it a major design challenge, namely an inherent wide dynamic variation between a signal’s peak and the average power. The peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) leads to inefficient transmission performance. That’s because the OFDM waveform is created by the sum of multiple sinusoidal signals that can exhibit constructive…
Experiments bring hope for 6G above 100 GHz
Efforts to explore and “unlock” this frequency region require an interdisciplinary approach with high-frequency RF semiconductor technology. The THz region also shows great promise for many application areas ranging from imaging to spectroscopy to sensing.
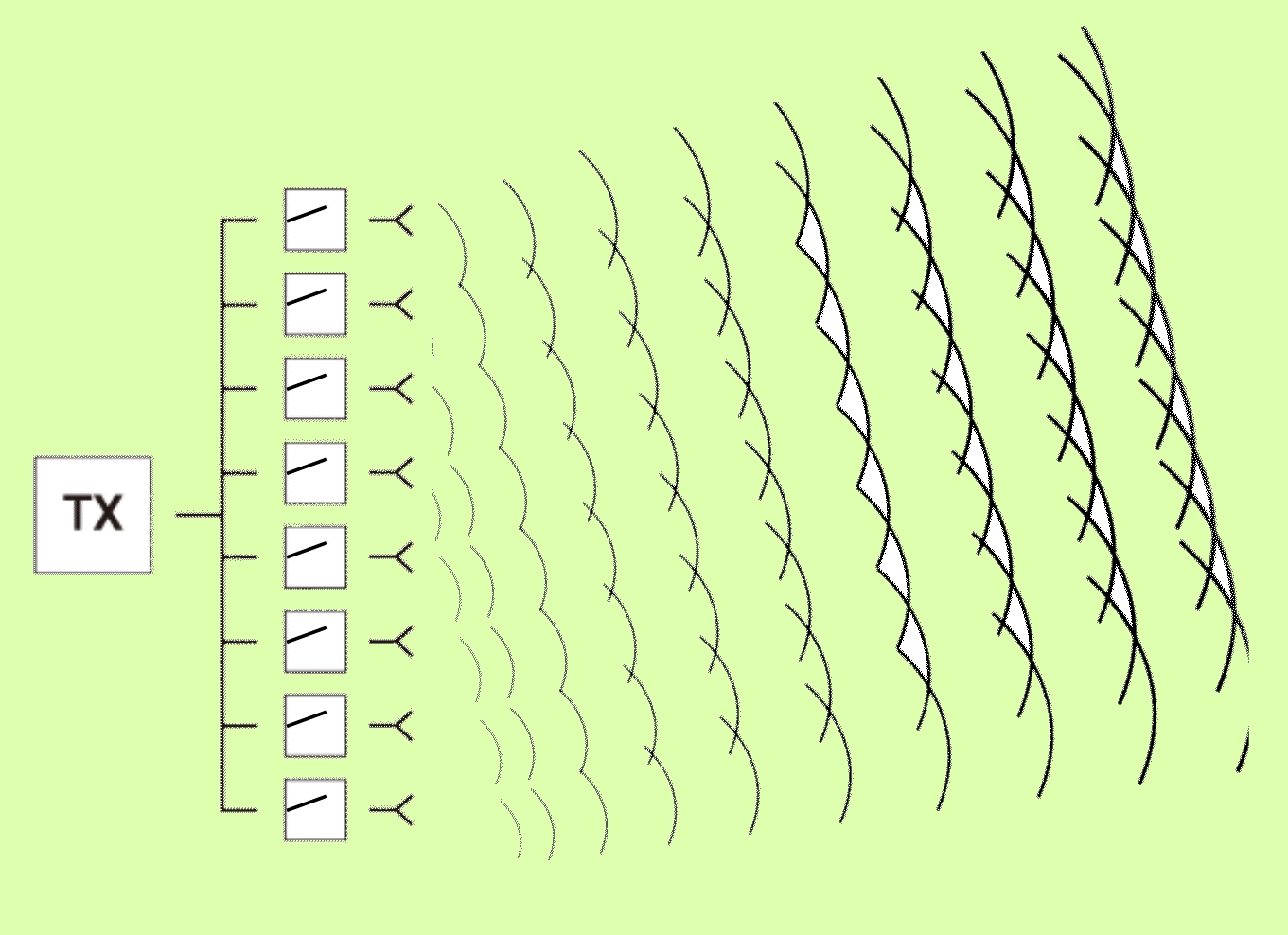
Test methods for mmWave AiP designs bring tradeoffs
Engineers have several mmWave over-the-air test methods available for evaluating phased-array antennas used in antenna-in-package designs. Each has pros and cons.
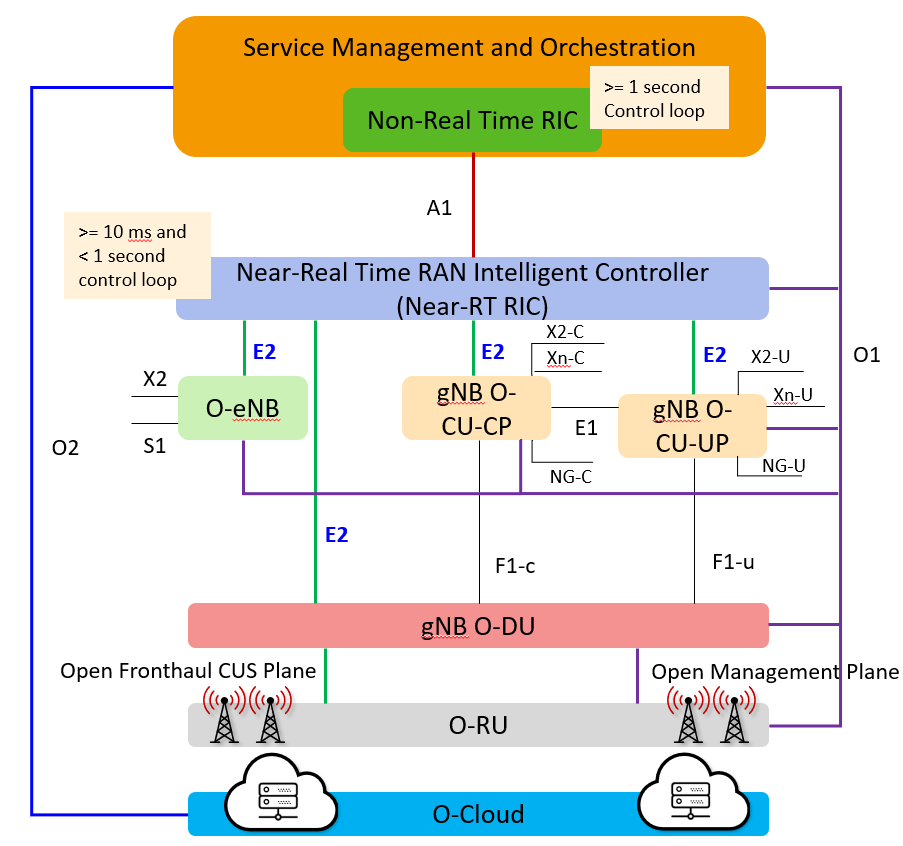
How does 5G’s O-RAN E2 interface work?
Open radio-access networks (Open RAN) disaggregate a cell tower’s baseband unit into three units. The 5G Open RAN architecture specified by 3GPP separates functions into a centralized unit (CU) and distributed unit (DU), where these functions were otherwise contained in the baseband unit, which also included the radio. These units provide network operators with the…
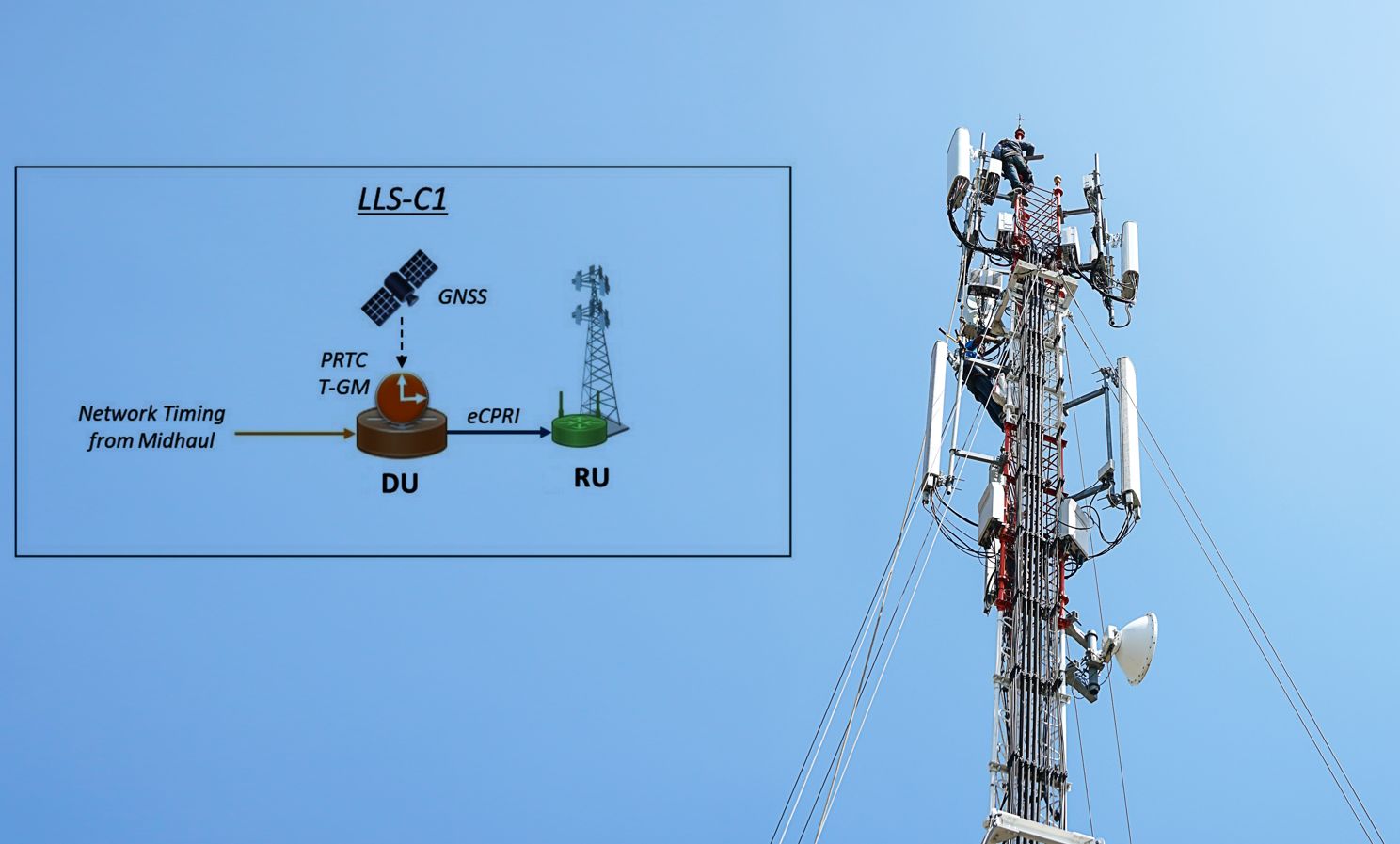
How IEEE 1588 synchronizes 5G Open RAN
The three units that comprise Open RAN 5G networks need precise timing to properly interoperate. Standards dictate what is needed, but it’s up to design engineers to properly implement timing circuits. 5G networks, with their promise of increased bandwidth and improved responsiveness, impose new challenges on equipment designers and network architects. One such challenge comes…
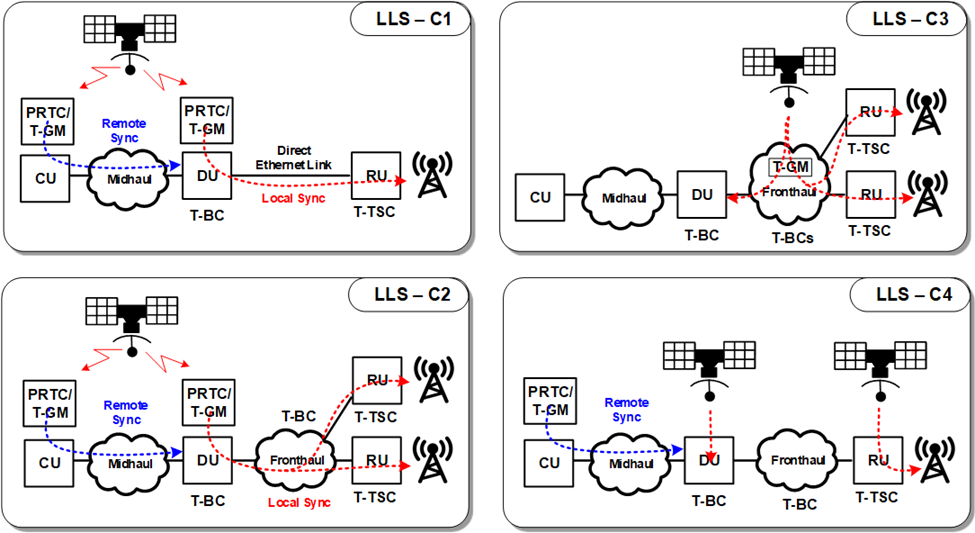
Open RAN networks pass the time
Network elements must meet certain frequency, phase, and time requirements to ensure proper end-to-end network operation. Synchronization architectures defined by the O-RAN alliance dictate how Open RAN equipment can meet these requirements. Open RAN continues to attract interest from service providers looking to reduce cost, improve competition, and drive technology innovation. The desire for a…
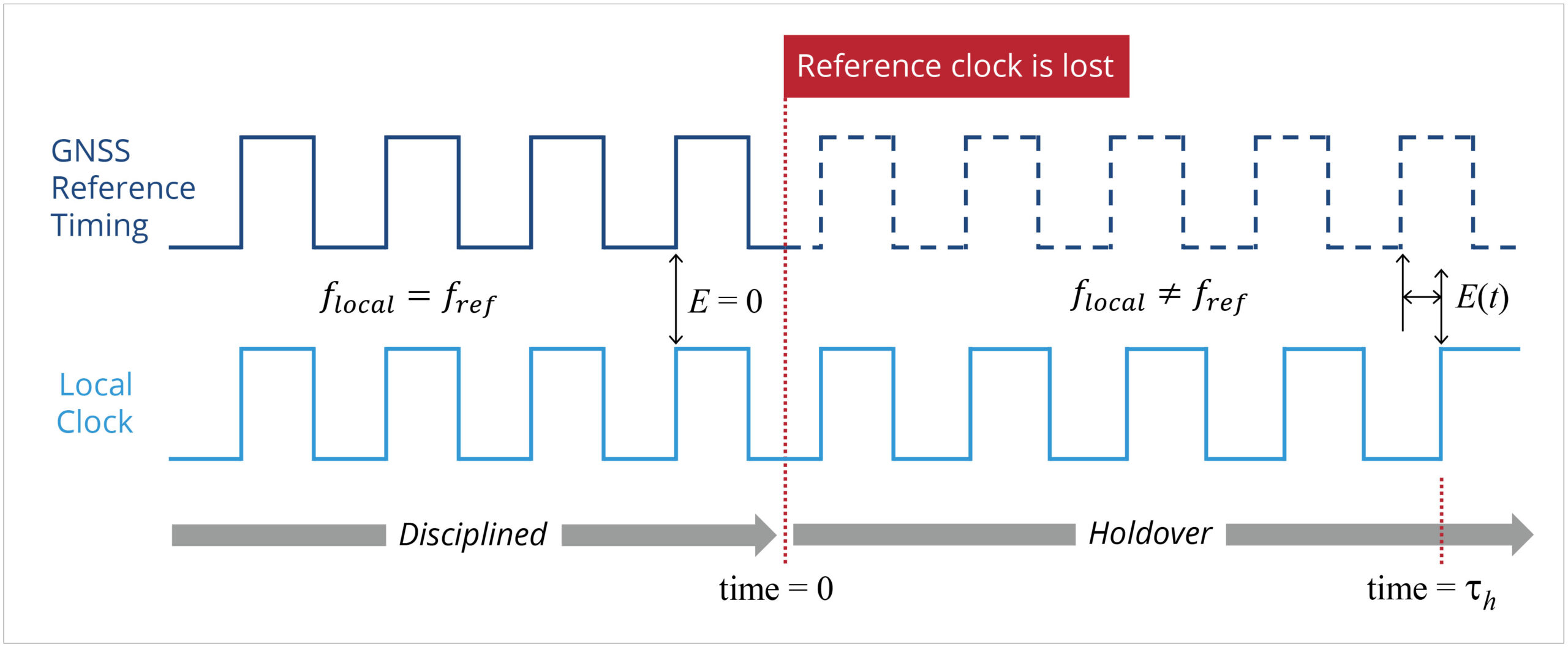
How timing propagates in a 5G network
5G’s high speeds place extreme demands on the components that maintain accurate time. Compliance with industry timing standards calls for accuracy in the face of temperature changes, shock, and vibration.